List of Drugs Stored in Refrigerator⁚ A Comprehensive Guide
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of medications requiring refrigeration, emphasizing proper storage, handling, and monitoring to maintain efficacy and safety․ It includes a list of common refrigerated drugs, best practices, and safe disposal methods․ Access additional resources for detailed information on pharmaceutical storage․
Types of Medications Requiring Refrigeration
Numerous medications necessitate refrigeration to preserve their stability and potency․ These include, but aren’t limited to, several biological agents such as vaccines and insulin․ Many antibiotics, particularly those in liquid form, require cold storage to prevent degradation․ Certain eye drops, nasal sprays, and topical creams also fall under this category․ Injectable medications, especially those containing proteins or peptides, often require refrigeration to maintain their structural integrity and biological activity․ Growth hormones, often used in the treatment of growth disorders, are another example․ Chemotherapy drugs, known for their sensitivity to temperature fluctuations, frequently demand cold storage to prevent their breakdown or loss of efficacy․ Finally, certain specialized formulations, like some reconstituted powders or suspensions, might need refrigeration as part of their storage instructions․
It’s crucial to always check the specific storage requirements listed on each medication’s label or package insert․ This information is critical for ensuring both the efficacy and safety of the medicine․ Failure to adhere to proper storage instructions can lead to the medication becoming ineffective or even unsafe for use․
Importance of Proper Storage Temperature
Maintaining the correct storage temperature for medications is paramount for ensuring their efficacy and safety․ Many pharmaceuticals are sensitive to temperature fluctuations, and exposure to extreme heat or cold can lead to degradation, rendering them ineffective or potentially harmful․ Improper storage can alter the chemical structure of the drug, reducing its potency and potentially creating toxic byproducts․ For instance, vaccines, which are temperature-sensitive biological products, can lose their effectiveness if exposed to temperatures outside the recommended range․ Similarly, certain medications that require refrigeration may experience a reduction in potency or undergo chemical changes when stored at room temperature․ This can result in a lower therapeutic effect or increased risk of adverse reactions․ Consistent adherence to recommended storage temperatures is crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of medications․
Moreover, proper storage ensures the medication remains stable until its expiration date, minimizing waste and maximizing the benefit of the investment in the pharmaceutical․ Strict temperature control is particularly crucial for medications with short shelf lives or those requiring specific storage conditions, such as those that need to be kept frozen or refrigerated․
Maintaining the Cold Chain⁚ Transportation and Handling
Maintaining the cold chain is critical for temperature-sensitive medications, ensuring their potency and safety throughout transportation and handling․ This involves using appropriate packaging and transportation methods to preserve the required temperature range from the manufacturer to the point of use․ For example, insulated containers with ice packs or gel packs are commonly employed to maintain the cold chain during shipment and delivery of vaccines or other refrigerated medications․ These containers help to buffer temperature fluctuations and prevent exposure to extreme temperatures․ Proper handling procedures are equally important․ This includes minimizing the time medications spend outside of refrigeration, avoiding direct sunlight or extreme temperatures, and using appropriate storage equipment such as medical-grade refrigerators or freezers at each stage of the process․ Regular temperature monitoring throughout the cold chain is also crucial to ensure that the medications remain within the specified temperature range․
Documentation of temperature throughout the entire process is essential for traceability and quality assurance․ Any deviations from the recommended temperature range should be carefully recorded and investigated to determine the cause and prevent future occurrences․ The cold chain’s integrity is crucial for maintaining product quality and patient safety, ensuring the medication’s effectiveness and minimizing the risk of adverse events․
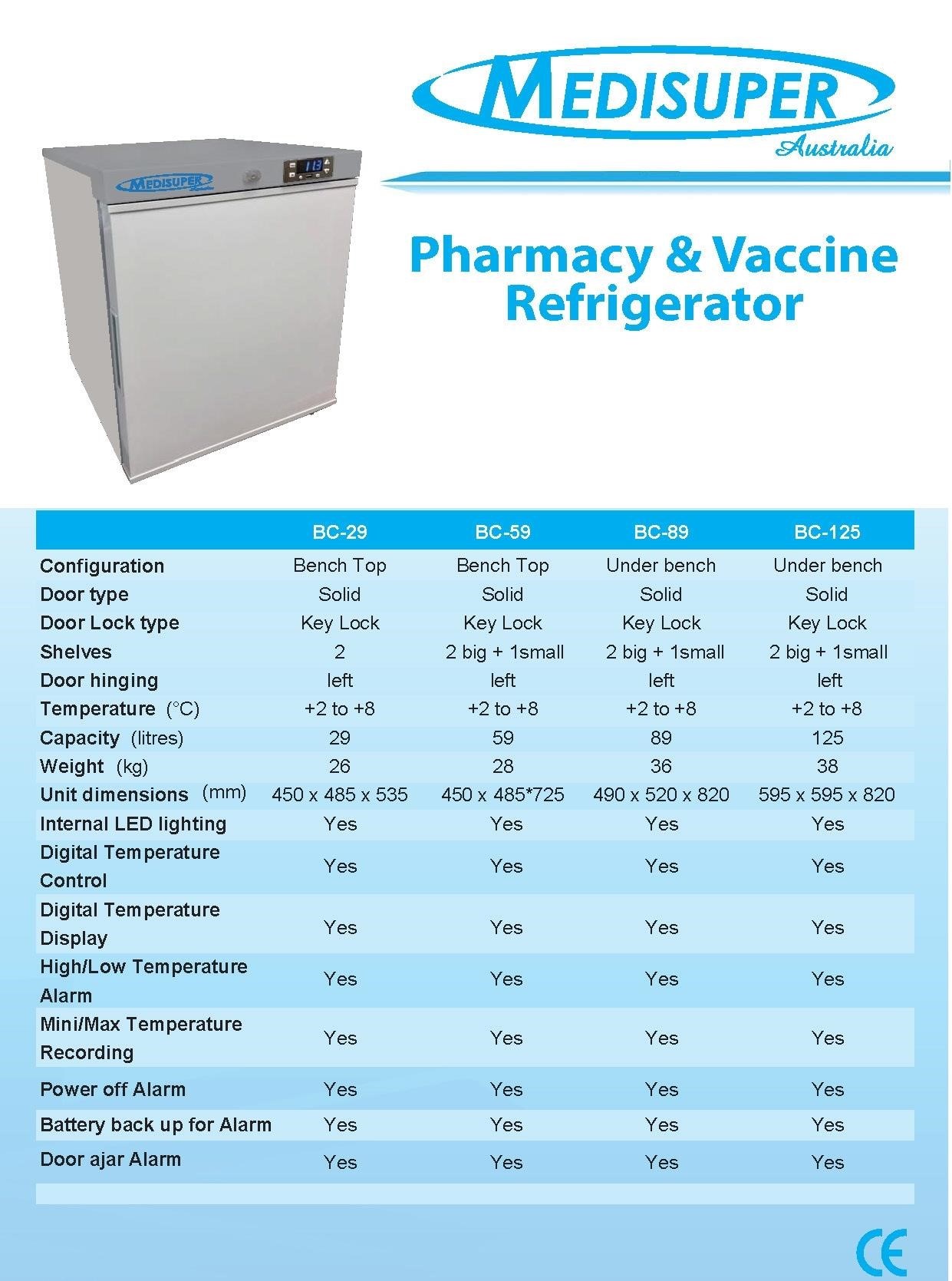
Medical-Grade Refrigerators for Pharmaceutical Storage
Medical-grade refrigerators are specifically designed for the safe and reliable storage of pharmaceuticals, vaccines, and other temperature-sensitive medications․ Unlike standard household refrigerators, these units provide precise temperature control and monitoring, ensuring that medications are maintained within the required temperature range․ They often feature advanced features such as digital temperature displays, audible and visual alarms for temperature excursions, and data logging capabilities to record temperature fluctuations over time․ This ensures compliance with regulatory guidelines and helps to maintain the quality and efficacy of the stored medications․
Many medical-grade refrigerators are designed with features to minimize temperature fluctuations caused by door openings or ambient temperature changes․ Some models include features like forced-air circulation to ensure uniform temperature distribution throughout the unit․ The construction of these refrigerators is also robust, with insulated walls and doors to help maintain the set temperature․ Choosing the appropriate size and model of medical-grade refrigerator depends on the volume of medications to be stored and the specific storage requirements of the individual products․ Regular maintenance and calibration of these units are crucial to ensure their continued performance and reliability․ Properly functioning medical-grade refrigerators are essential for maintaining the quality and safety of stored medications․
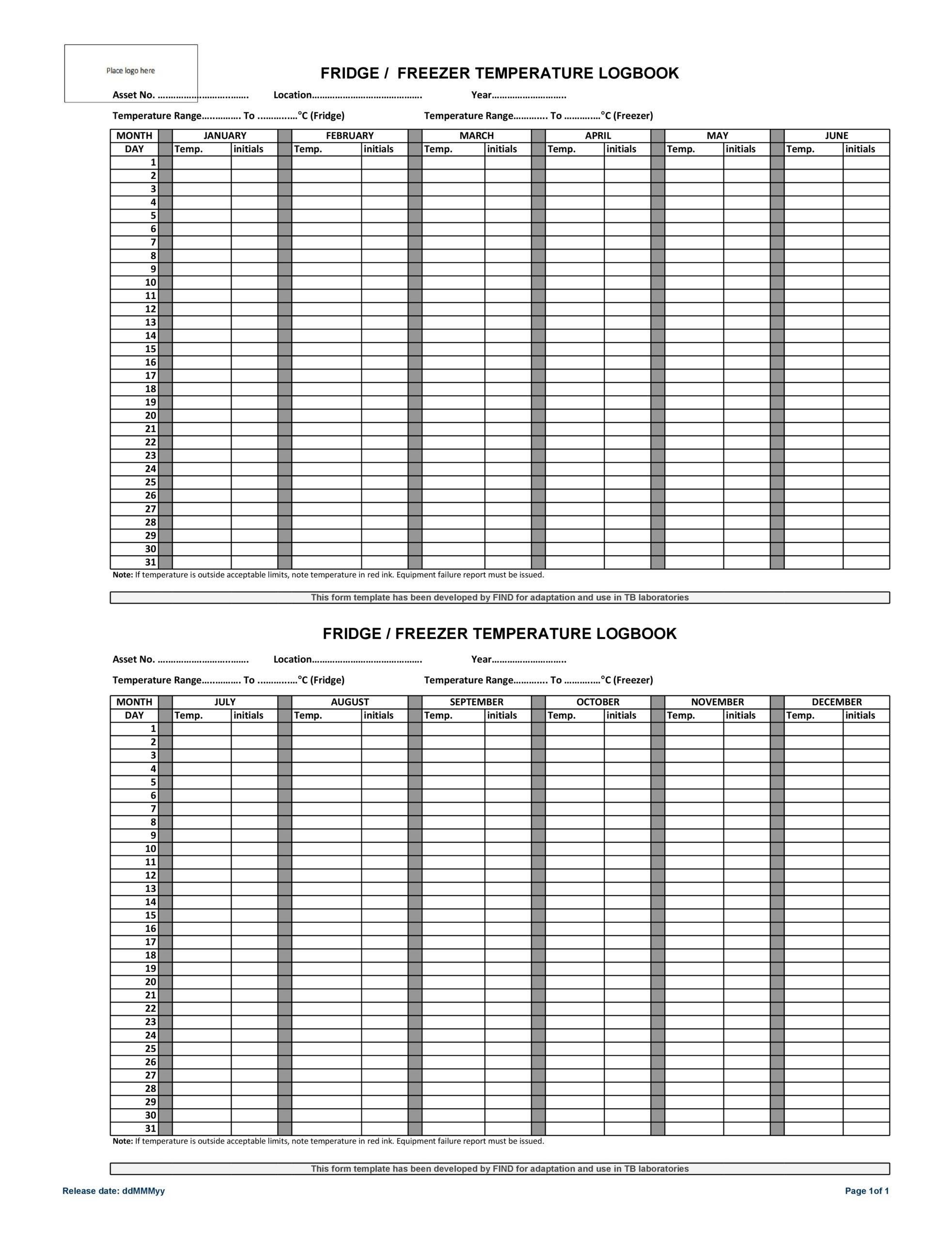
Monitoring and Recording Refrigerator Temperature
Consistent monitoring and accurate recording of refrigerator temperatures are critical for ensuring the stability and efficacy of stored medications․ This involves using reliable thermometers, preferably those with digital displays and data logging capabilities, placed strategically within the refrigerator to accurately reflect the temperature throughout․ Daily temperature checks are recommended, with more frequent checks during periods of potential temperature fluctuation, such as power outages or extreme ambient temperatures․ A detailed log should be maintained, recording the date, time, and temperature readings․ Any deviations from the recommended temperature range should be immediately investigated and documented, along with any corrective actions taken․
Temperature monitoring systems can range from simple manual checks with a thermometer to sophisticated electronic systems that automatically record and alert personnel to temperature excursions․ These systems can provide valuable data for quality control and regulatory compliance․ It’s crucial to adhere to established protocols for handling and investigating temperature deviations, following established procedures for reporting and addressing any potential impact on medication stability․ Thorough documentation of all temperature monitoring activities is essential for demonstrating compliance with regulatory guidelines and maintaining the integrity of stored medications, protecting patient safety and treatment efficacy․
Common Medications Requiring Refrigeration⁚ A List
Many medications require refrigeration to maintain their potency and stability․ This list is not exhaustive, and it’s crucial to always refer to the specific storage instructions provided by the manufacturer on the medication’s label or packaging․ Common examples include various insulin products (e․g․, Humalog, Lantus), numerous vaccines (influenza, MMR, etc․), some eye and ear drops, certain injectable medications (e․g․, growth hormones, certain chemotherapy drugs), and specific topical creams and gels․ Many biological medications, including monoclonal antibodies, often need cold storage․ Additionally, reconstituted powders, once mixed with a diluent, frequently necessitate refrigeration․ Remember that the storage requirements can vary based on the specific formulation of the drug and the manufacturer’s recommendations․
Always double-check individual product labeling for precise storage instructions․ This list serves as a general guideline, but the ultimate authority for storage conditions is the information found on the medicine’s packaging․ Failing to adhere to these requirements can compromise the drug’s efficacy and potentially lead to adverse effects․ Maintaining a consistent and accurate record of medication storage conditions is essential for maintaining patient safety and optimal treatment outcomes․ Regular review of medication storage procedures is paramount to ensuring ongoing compliance and adherence to best practices․
Storage Guidelines and Best Practices
Proper storage of refrigerated medications is crucial for maintaining their efficacy and safety․ To ensure optimal storage, designate a specific area within the refrigerator solely for medications, clearly labeled and easily accessible to authorized personnel only․ Avoid placing medications in the warmest (door) or coldest (bottom shelf) areas, opting for the more stable upper shelves․ Always check the refrigerator’s temperature regularly, ideally using a calibrated thermometer, to ensure it remains within the recommended range of 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C)․ Maintain accurate records of temperature checks, noting any deviations or inconsistencies․ When storing medications, follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely․ Some products might require specific placement, such as upright or lying flat․ Proper labeling of each medication container is essential, clearly indicating the drug’s name, strength, expiration date, and date of opening (if applicable)․ Regularly review expiration dates and promptly discard any expired medications following appropriate disposal guidelines․
Before placing medications in the refrigerator, ensure they are properly sealed to prevent moisture damage and contamination․ Avoid storing medications near strong-smelling substances that could potentially affect their stability or integrity․ Regularly inspect the refrigerator for any signs of damage or malfunction, and promptly report any issues to the relevant authorities․ Adherence to these guidelines ensures the safety and effectiveness of your refrigerated medications․ It is vital to follow all local regulations and guidelines regarding medication storage and handling․
Risks of Improper Storage⁚ Impact on Efficacy and Safety
Improper storage of refrigerated medications poses significant risks, potentially compromising their efficacy and safety․ Exposure to temperatures outside the recommended range (36°F to 46°F or 2°C to 8°C) can lead to degradation of the active pharmaceutical ingredients, reducing the drug’s potency․ This diminished potency may render the medication ineffective, failing to provide the intended therapeutic effect․ In some cases, improper storage can even lead to the formation of harmful byproducts or the alteration of the drug’s chemical structure, potentially causing adverse reactions or toxicity when administered․ Furthermore, fluctuating temperatures can accelerate the degradation process, shortening the medication’s shelf life and increasing the risk of spoilage․ Exposure to light, moisture, or extreme temperatures can also negatively affect the physical properties of certain medications, causing changes in consistency, color, or odor, which might indicate degradation․ These changes can impact the drug’s stability, absorption, and overall effectiveness․ The consequences of improper storage can range from treatment failure to serious health complications, emphasizing the critical importance of adhering to recommended storage guidelines․ Careful monitoring and adherence to best practices are crucial for ensuring patient safety and treatment success․
Shelf Life and Expiration Dates of Refrigerated Medications
Understanding the shelf life and expiration dates of refrigerated medications is crucial for ensuring their efficacy and safety․ Expiration dates, clearly indicated on the medication packaging, represent the manufacturer’s guarantee of potency and stability under proper storage conditions․ Once a medication’s expiration date passes, its potency may decrease, potentially rendering it ineffective․ In some instances, degraded medications might even become harmful if ingested․ However, the expiration date assumes proper storage throughout the product’s shelf life․ Improper storage, such as exposure to fluctuating temperatures or excessive light, can significantly shorten a medication’s effective lifespan, potentially making it unsafe to use well before its printed expiration date․ Always check the packaging for specific storage instructions and monitor the medication’s condition for any signs of degradation, such as changes in color, texture, or odor․ If any unusual changes are observed, discard the medication and obtain a new supply․ Remember, using expired or improperly stored medications carries significant risks and should be avoided to ensure patient safety and treatment effectiveness․ Consult with a healthcare professional or pharmacist if you have any concerns about a medication’s shelf life or expiration date․
Safe Disposal of Expired Refrigerated Medications
Safe disposal of expired or unwanted refrigerated medications is essential to protect public health and the environment․ Never flush medications down the toilet or drain, as this can contaminate water supplies․ Instead, follow these guidelines⁚ First, check the medication’s label or packaging for specific disposal instructions․ Some medications may require special handling․ If specific instructions are not provided, mix the medication with an undesirable substance, such as used coffee grounds or kitty litter․ This makes the medication less appealing and prevents accidental ingestion․ Place the mixture in a sealed, non-recyclable container (such as a sealed plastic bag), and discard it in your household trash․ For controlled substances (narcotics, etc․), contact your local law enforcement or pharmacy for safe disposal options; they may offer take-back programs․ Many communities organize medication take-back events where you can safely dispose of unwanted medications, including those requiring refrigeration․ Check your local health department’s website or contact your pharmacist to find out about scheduled events near you․ Proper disposal prevents accidental poisoning, particularly among children and pets, and protects the environment from harmful chemical contamination․ Always prioritize safe and responsible medication disposal practices․
Resources and Further Information
For comprehensive and up-to-date information on medication storage, consult your pharmacist or healthcare provider․ They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific medications and health needs․ The FDA (Food and Drug Administration) website offers valuable resources on drug safety and handling, including storage guidelines․ Look for their publications and fact sheets on proper medication storage and disposal․ Professional organizations like the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) also provide detailed information on pharmaceutical storage, particularly regarding vaccines and other temperature-sensitive medications․ Their websites offer guidelines, best practices, and resources for healthcare professionals․ Additionally, many reputable medical websites and journals publish articles and studies on medication stability and storage․ Searching for relevant keywords, such as “medication storage guidelines,” “refrigerated medication stability,” or “pharmaceutical cold chain,” will yield numerous results․ Remember to always verify the credibility and accuracy of the information sources you consult․ Prioritize information from official government agencies, professional organizations, and peer-reviewed publications․